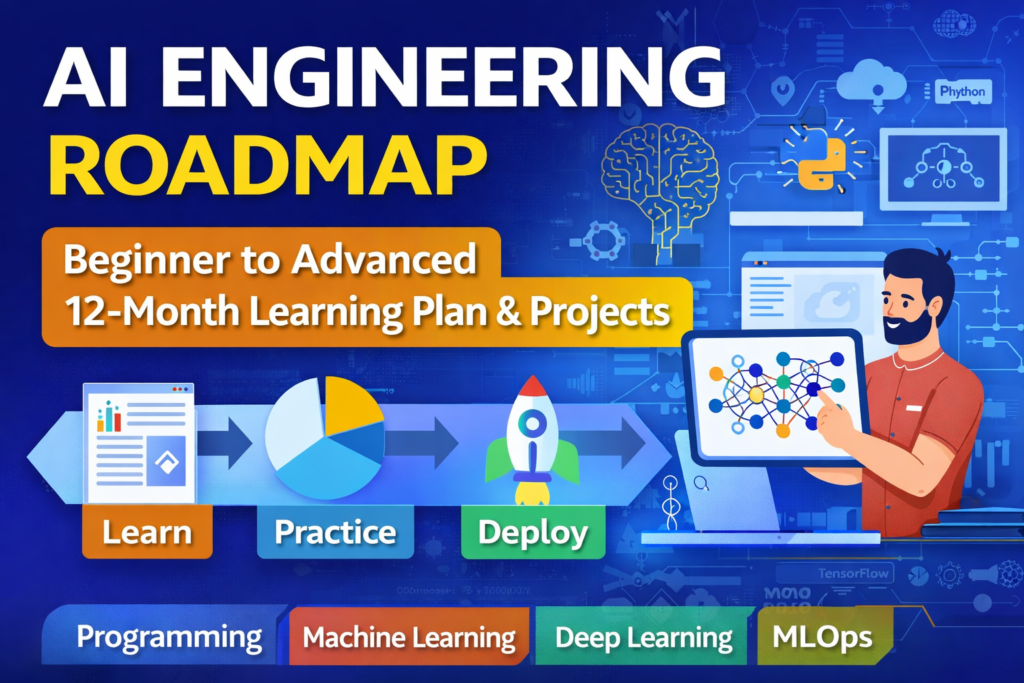
AI Engineering Roadmap is a structured guide designed to help beginners become professional AI engineers through a clear 12-month learning plan and real-world projects.
Artificial Intelligence Engineering is not a single skill—it is a career discipline that combines programming, mathematics, data engineering, machine learning, system design, and production deployment. This roadmap explains what to learn, why to learn it, and how it connects to real-world AI systems.
1. Understanding AI Engineering (Conceptual Foundation)


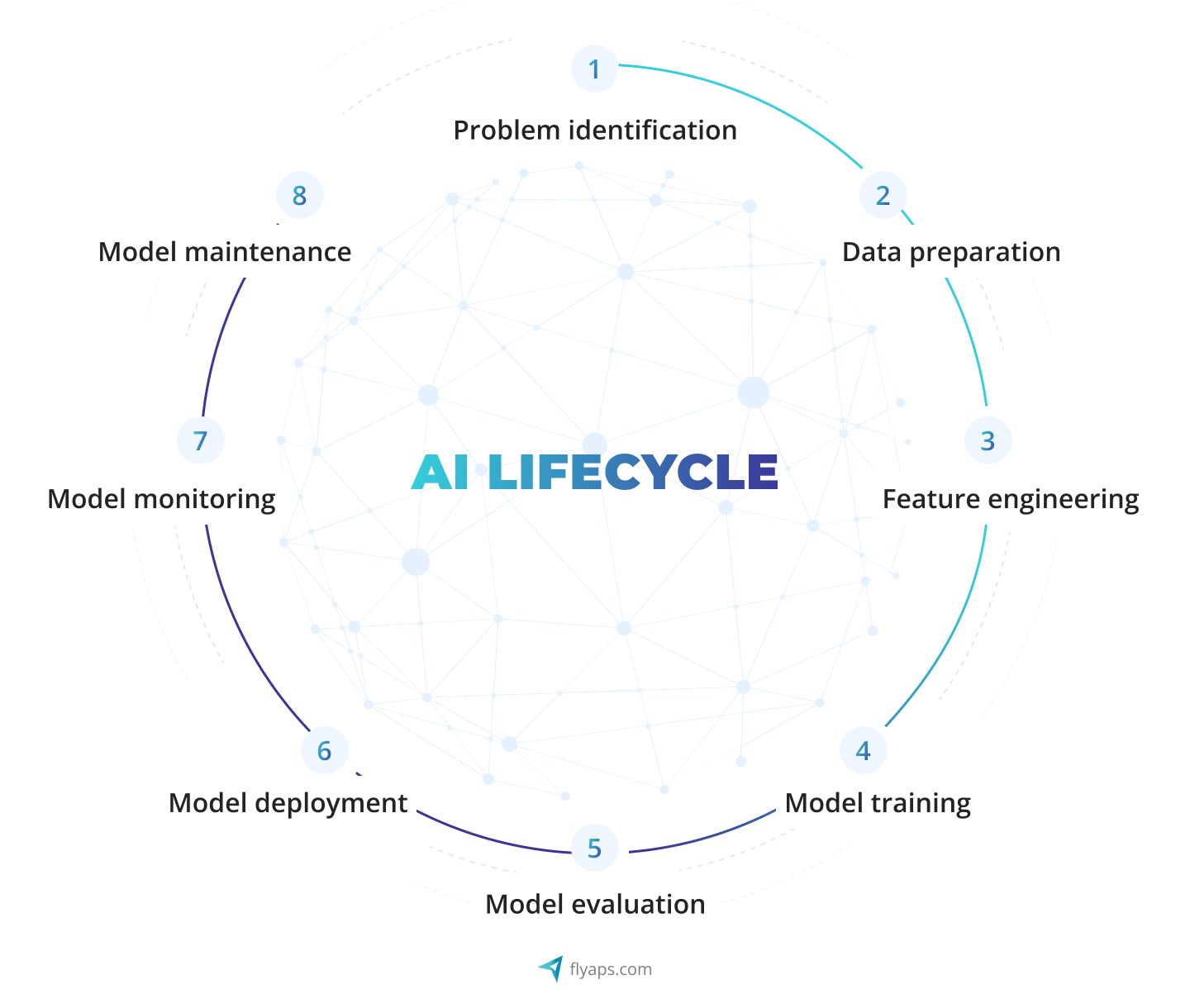
AI Engineering focuses on building intelligent systems that operate reliably in production, not just experimental models.
What AI Engineering Really Means
An AI Engineer is responsible for:
- Translating business problems into AI solutions
- Designing data pipelines
- Training and evaluating models
- Deploying models into real systems
- Monitoring performance over time
This role differs from:
- Data Scientists (focus on analysis and experiments)
- Researchers (focus on theory and innovation)
AI Engineers focus on execution, scalability, and reliability.
Core AI Categories Explained
- Artificial Intelligence: The umbrella concept of machine intelligence
- Machine Learning: Algorithms that learn patterns from data
- Deep Learning: Neural networks that learn complex representations
- NLP: Machines understanding human language
- Computer Vision: Machines interpreting images and video
Understanding these distinctions is critical for choosing the correct tools.
2. Programming Fundamentals (Technical Backbone)

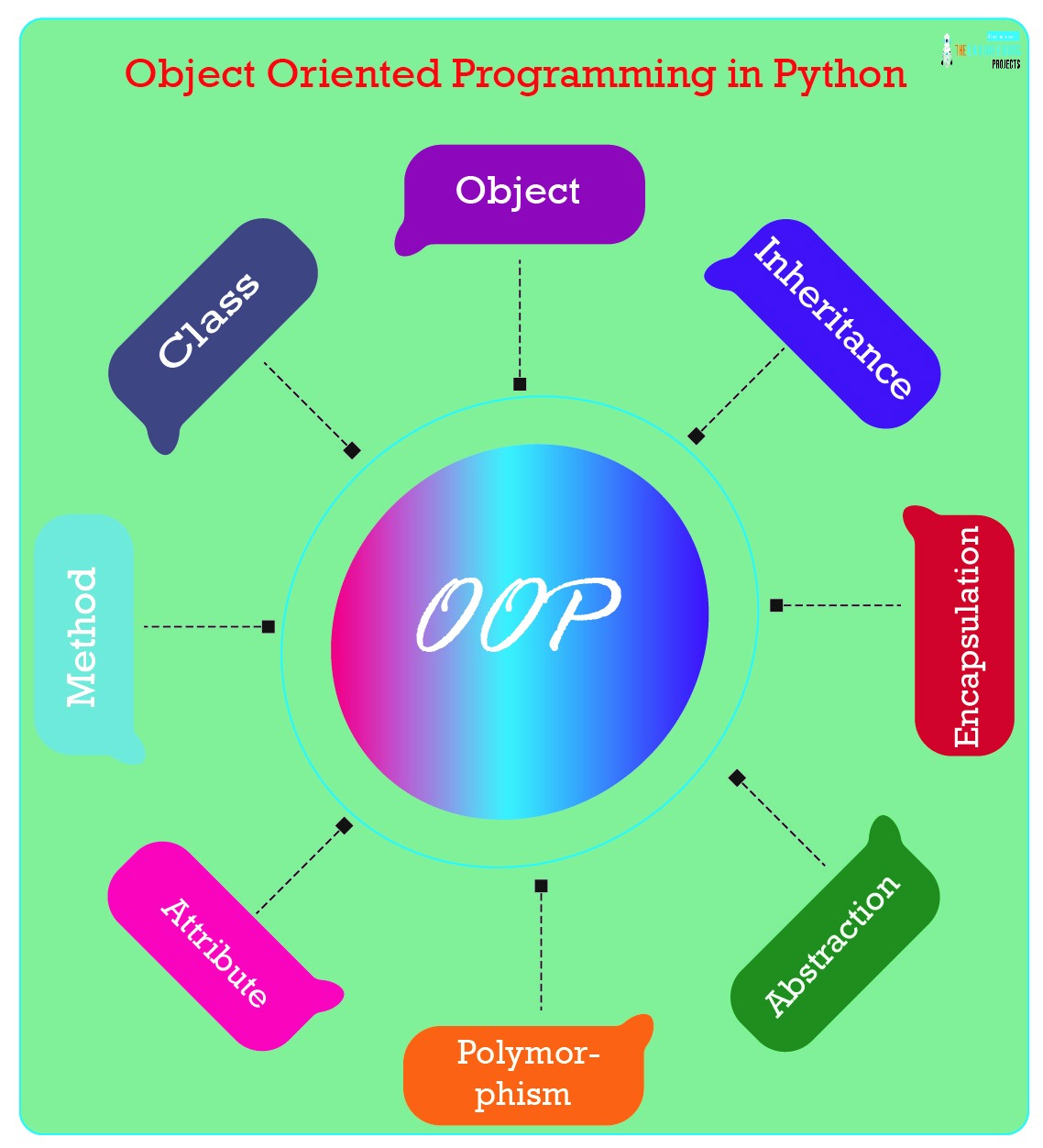

Programming is the primary working language of AI Engineering.
Why Python Is Essential
Python is preferred because it:
- Has readable syntax
- Offers vast AI libraries
- Integrates easily with cloud and APIs
Core Programming Skills Required
You must master:
- Control flow (loops, conditions)
- Functions and modular design
- Object-Oriented Programming (classes, inheritance)
- Error handling and debugging
- File handling and APIs
AI-Critical Libraries
- NumPy: numerical computation
- Pandas: structured data manipulation
- Matplotlib / Seaborn: visualization
- Requests / FastAPI: model APIs
Without strong Python skills, AI theory becomes unusable.
3. Mathematics for AI Engineers (Decision Logic)


Mathematics is the reason models behave the way they do.
Linear Algebra
Used in:
- Neural network computations
- Feature transformations
- Embeddings and vectors
Key ideas:
- Vectors and matrices
- Matrix multiplication
- Eigenvalues (intuition)
Probability & Statistics
Used for:
- Model uncertainty
- Predictions
- Evaluation metrics
Key concepts:
- Random variables
- Distributions
- Bayesian thinking
Calculus
Used in:
- Model optimization
- Training neural networks
You mainly need:
- Partial derivatives
- Gradient descent intuition
Focus on understanding behavior—not memorization.
4. Data Handling & Feature Engineering (AI Fuel)


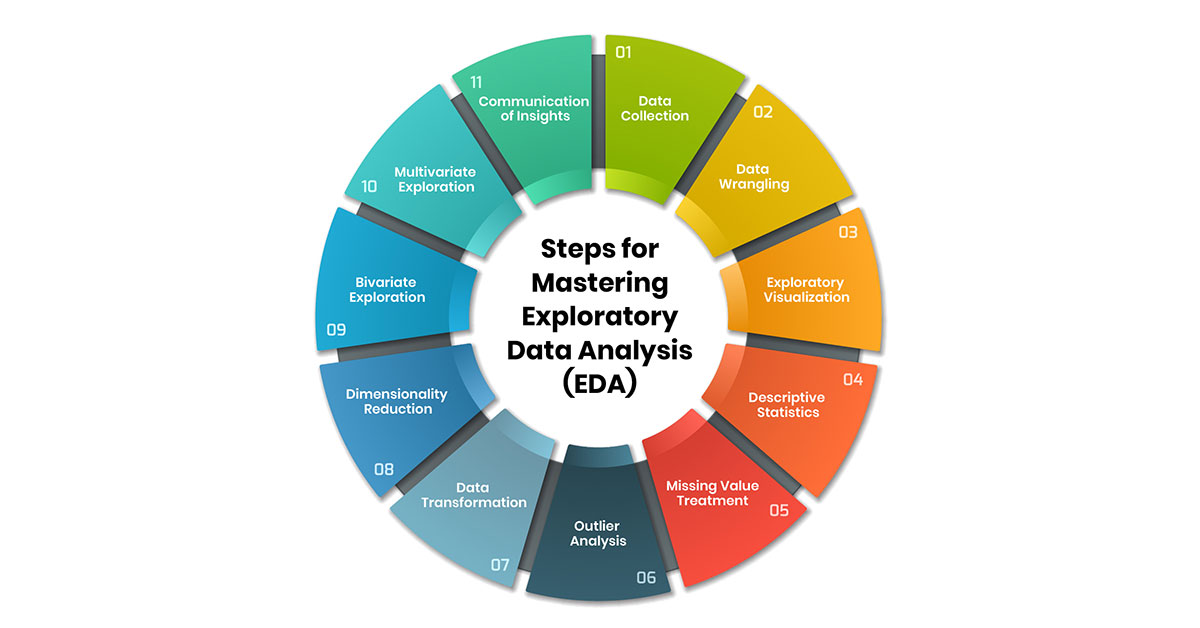
Data quality directly determines AI performance.
Data Cleaning
AI Engineers must:
- Handle missing values
- Remove duplicates
- Correct inconsistent formats
- Detect outliers
Feature Engineering
This is where engineering intelligence happens:
- Transform raw data into meaningful inputs
- Encode categories
- Normalize numerical values
- Create domain-specific features
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
EDA helps you:
- Understand distributions
- Detect bias
- Identify correlations
Bad features = bad models, regardless of algorithm strength.
5. Machine Learning Algorithms (Predictive Core)



Machine Learning allows systems to learn from data rather than rules.
Supervised Learning
Used when labeled data exists:
- Regression → predictions
- Classification → decisions
Algorithms:
- Linear/Logistic Regression
- Decision Trees
- Random Forest
- Gradient Boosting
Unsupervised Learning
Used when labels do not exist:
- Clustering
- Dimensionality reduction
Algorithms:
- K-Means
- PCA
Model Evaluation
AI Engineers must understand:
- Accuracy vs precision vs recall
- Overfitting vs underfitting
- Cross-validation
Models must generalize—not memorize.
6. Deep Learning & Neural Networks (Advanced Intelligence)


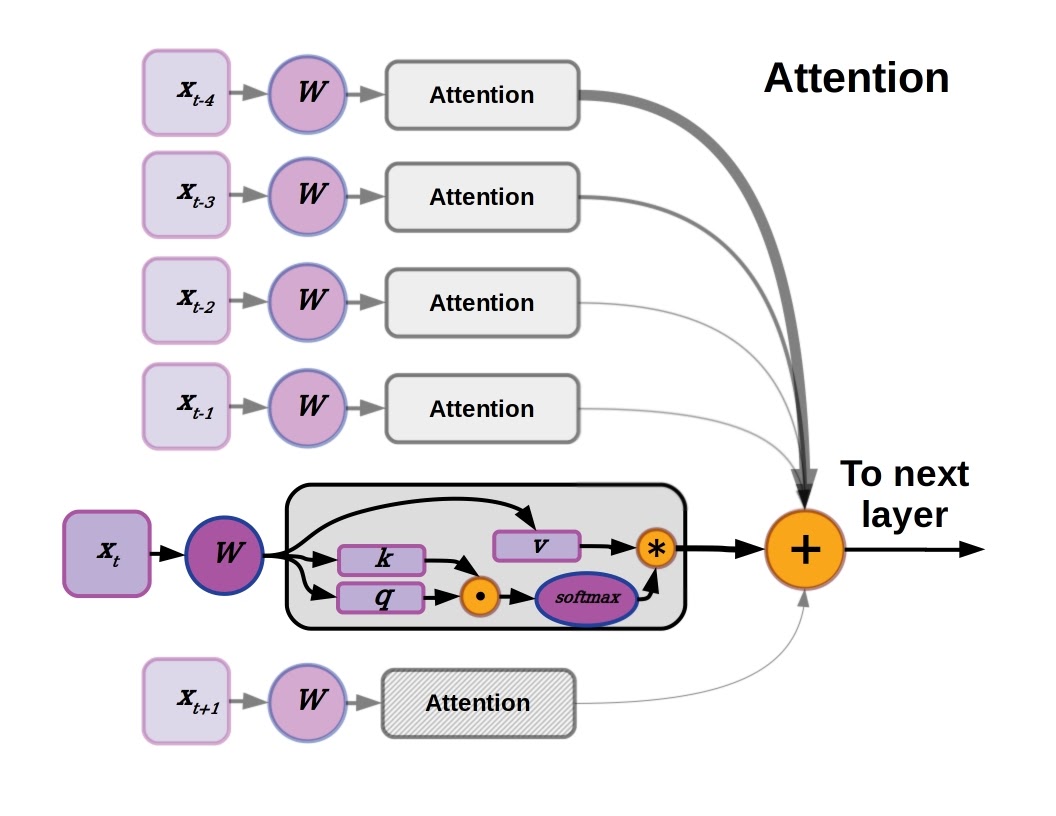
Deep Learning handles complex, unstructured data.
Neural Network Basics
- Layers
- Weights
- Activation functions
- Loss functions
Architectures
- CNNs: image processing
- RNNs: sequence data
- Transformers: language & generative AI
Frameworks
- PyTorch (research & production)
- TensorFlow (enterprise systems)
Deep learning requires compute power and discipline.
/what-is-artificial-intelligence/
7. Specialization Areas (Career Differentiation)

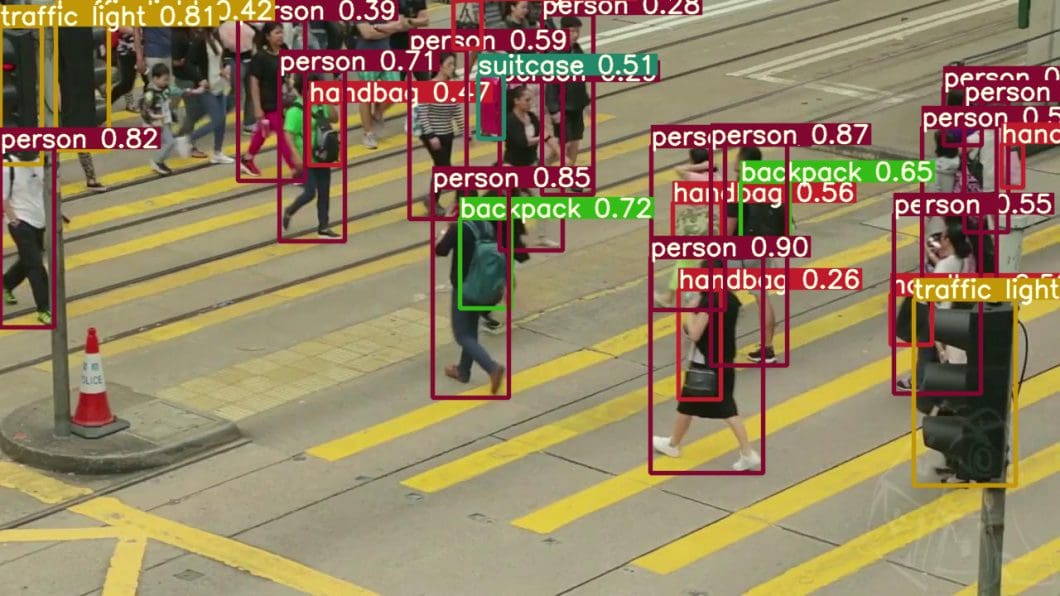

Specialization determines career direction and salary range.
NLP
- Chatbots
- Search engines
- Text analysis
Computer Vision
- Facial recognition
- Medical imaging
- Surveillance systems
Reinforcement Learning
- Robotics
- Game AI
- Autonomous control
Generative AI
- Text generation
- Image synthesis
- Audio generation
Depth matters more than breadth.
8. MLOps & Deployment (Production Reality)


A model not deployed is not engineering.
Deployment Skills
- REST APIs
- Containerization
- Cloud services
- CI/CD pipelines
Monitoring
- Performance decay
- Data drift
- Retraining schedules
This is where AI Engineers differ from learners.
9. AI Ethics, Security & Governance (Trust Layer)


AI systems influence decisions affecting people.
Core Principles
- Fairness
- Transparency
- Privacy
- Accountability
Companies require engineers who reduce legal and ethical risk.
10. Portfolio, Projects & Career Execution

Required Projects
- End-to-end ML system
- Deployed AI application
- Real dataset with business logic
Career Readiness
- GitHub repositories
- System design interviews
- Continuous learning mindset
Final Conclusion
AI Engineering is a long-term professional discipline, not a shortcut skill. Success depends on:
- Strong fundamentals
- Real-world projects
- Deployment experience
- Ethical awareness
HERE IS THE ROADMAP STEP BY STEP: Beginner to Advanced 12-Month Learning Plan
AI Engineering Roadmap: Beginner to Advanced 12-Month Learning Plan with Projects
Artificial Intelligence Engineering is a career focused on building, deploying, and maintaining intelligent systems in real-world production environments. This comprehensive AI Engineering roadmap provides a structured, step-by-step journey from beginner to advanced level, combining theory, hands-on projects, and production-grade skills over a 12-month timeline.
Phase 1: Foundations of AI Engineering (Months 1–3)
Month 1: Programming Fundamentals and AI Mindset
The foundation of AI Engineering begins with strong programming skills. Python is the primary language used due to its simplicity, scalability, and extensive AI ecosystem. During this stage, learners focus on writing clean, readable code and understanding basic software engineering principles.
- Python fundamentals and object-oriented programming
- Git and GitHub version control
- Basic Linux command-line operations
Project: Python automation script for data cleaning and preprocessing.
Month 2: Data Analysis and Statistics
AI systems depend heavily on data quality. In this phase, learners gain the ability to explore, analyze, and interpret datasets using Python libraries such as Pandas and NumPy. Statistical understanding helps validate insights and detect bias.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Data visualization
- Basic probability and statistics
Project: Real-world dataset analysis with visual insights.
Month 3: Mathematics for Machine Learning
Mathematics forms the logic behind how models learn. Instead of deep theory, the focus is on intuitive understanding of linear algebra, probability, and optimization techniques used in AI.
Project: Implement linear regression using NumPy from scratch.
AI Engineering Roadmap Phase 2: Core Machine Learning (Months 4–6)
Month 4: Supervised Machine Learning
Supervised learning enables machines to make predictions using labeled data. Learners understand regression, classification, and evaluation metrics essential for business decision-making.
- Linear and logistic regression
- Decision trees and ensemble methods
- Model evaluation metrics
Project: Predictive ML model with performance comparison.
Month 5: Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning helps uncover hidden patterns in unlabeled data. This is crucial for segmentation and anomaly detection.
Project: Customer or user segmentation using clustering techniques.
Month 6: End-to-End Machine Learning Pipeline
AI Engineers must build pipelines that handle data ingestion, training, validation, and model storage seamlessly.
Project: Full ML pipeline with experiment tracking.
AI Engineering Roadmap Phase 3: Deep Learning and Specialization (Months 7–9)
Month 7: Neural Networks and Deep Learning
Deep learning enables machines to understand complex patterns such as images, speech, and text. Learners explore neural network architectures and training strategies.
Project: Neural network classifier using PyTorch or TensorFlow.
Month 8: Specialization Track
At this stage, learners choose one specialization to deepen expertise:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Computer Vision
- Generative AI
Project: Domain-specific AI application.
Month 9: Model Optimization
Optimization improves model performance and efficiency through fine-tuning, regularization, and transfer learning.
Project: Optimized production-ready AI model.
AI Engineering Roadmap Phase 4: MLOps and Production Deployment (Months 10–12)
Month 10: Model Deployment
Deployment converts models into usable services. AI Engineers must know APIs, containers, and cloud basics.
Project: Deploy AI model as a REST API using FastAPI and Docker.
Month 11: MLOps and Monitoring
MLOps ensures reliability through automation, monitoring, and retraining strategies.
Project: Automated MLOps pipeline with monitoring.
Month 12: Capstone Project and Career Readiness
The final stage focuses on system design, ethical AI, and interview readiness.
Capstone: Full end-to-end AI product with real-world use case.
Final Outcomes After 12 Months
- Strong Python and Machine Learning foundation
- Hands-on Deep Learning and specialization experience
- Production deployment and MLOps skills
- Professional AI Engineer portfolio
Conclusion
This AI Engineering roadmap provides a complete transformation path from beginner to job-ready AI Engineer. By combining structured learning, real-world projects, and deployment experience, learners develop industry-relevant skills required by modern organizations.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence